IT Security Management Best Practices to Prevent Cyberattacks
Definition of IT Security Management
IT security management is the approach of an organization or a company to secure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their assets while safeguarding the same from cyberattacks. The IT security management team takes care of security analysis and IT operations and carries out security-related tasks. Every organization holds information that they intend not to expose or would not want to fall into the wrong hands. Security is critical to keep this data from being stolen or accessed by outsiders, regardless of how it is stored, physically or digitally. One should understand what the organization owns so that protection can be prioritized.
How IT Security is Managed at Proinf?
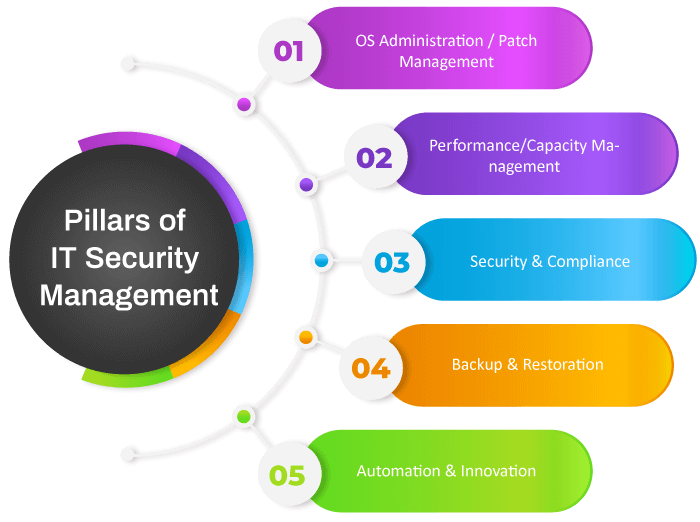
Businesses today collect and store huge amounts of data from their customers and their transactions. This data includes behavioral analytics, credit cards or payment-related information, usage data, healthcare analytics, passwords, personal information, and a lot more. The storage of all this has typically increased cyberattacks and information theft. This resulted in significant advancements in Information Security Management. To be an effective IT Security management provider, the five core pillars of IT security management should be properly understood.
- OS Administration and Patch Management
- Performance/Capacity Management
- Security & Compliance
- Backup & Restoration
- Automation & Innovation
The latest trends in cybersecurity in 2022
- The world has recognized the significance of cybersecurity.
- The top threat is almost always Data Breaches or Data Thefts
- Risks with IoT Devices which need IT and OT Security to keep them risk-free.
- The demand for IT security personnel has always remained above their supply
- Automation of cybersecurity has become a necessity
- There is exponential growth in cloud-based security issues
- Mobile devices are the major targets of cyberthreats
OS Administration and Patch Management
OS Administration or OS Hardening is a type of implementing security measures and patching for OSs such as Windows, Linux, and Unix. OS Administration typically includes:
- Ensuring the best security practices and secure configurations are followed.
- Updating OSs with patches and service packs
- Enabling endpoint protection, firewalls, and security extensions for OS
OS administration helps in reducing the risk of cyber attacks. To make it more effective, OS administration is always implemented alongside a backup process. This is an alternative strategy to ensure that copies of the original data and OS are readily available in case of any unexpected failure.
Each OS has its features and a list of some of the best practices that help in enhancing security for the OS:
- Service Packs - keeping programs updated by installing the latest versions. This dramatically reduces the risk of attacks on the OS and its applications.
- Patch Management - includes auditing the OS and applications on client systems are updated regularly
- Clean Programs - Deleting unused or unnecessary applications. Every installed application should be timely audited as it can be a potential entry point for a malicious attack.
- Access Control and Group Policies - restricting users to access files, networks, and resources. Access control management for user groups is a characteristic feature provided by both Windows and Linux.
- Security Templates - managing and enforcing security configurations centrally.
- Firewall Configuration - allowing traffic from approved IP addresses and ports. Any unnecessary open ports always represent a security loophole.
- Endpoint Protection - Windows Defender for Windows OS comes with this solution.
- Isolation - Ensuring sensitive data and applications are run on separate virtual machines or containers.
Performance Management
Performance Management involves auditing the assets and the infrastructure. This includes the disk space available, network, CPU, memory, etc. There are various ways to handle the performance of the assets. The general process at Proinf is:
Auditing
- Start with the crucial assets.
- Compile a life of cybersecurity infrastructure and performance-related assets that are utilized by all departments in the company.
- Choose an evaluation method.
- Score each asset based on a critical condition.
- Update with the necessary modifications to ensure a steady and smooth run.
Monitoring
- The next step is to carefully monitor for any potential security breaches.
- Based on the results, identify risky nodes and resource-consuming sectors.
Planning and Forecasting
- When the visibility of resources increases, it enhances their utilization and performance.
- This can make more informed decisions for the future.
- Change the infrastructure based on its usage and its capacity.
- Educate the employees on how to make the best of available resources.
- With a strong compilation and cooperation from employees, organizations worry less about cybersecurity and performance.
Security & Compliance
Organizations have been mandated to maintain a system that can protect the privacy and security of their data. There are several reasons that IT Security Compliance standards are implemented and monitored. These regulations have been developed to improve an organization's IT Security strategies by implementing best practices based on the type of data they hold. Non-compliance with these standards might result in consequences like data breaches, theft, and loss.
Some key benefits of Security and Compliance standards include:
- Business security can be increased resulting in a reduction of threats (both internal and external)
- Financial losses can be drastically reduced due to cyberattacks and associated costs like repair expenses and legal fees.
- Improved security
- Customers trust the business as they understand that their data is safe.
Backup & Restoration
As many IT firms react to incidents, they believe in having a firewall or protecting the network or endpoint software is the best strategy. While these provide the best strategies partially, the priority should always be to know the most sensitive data and where it is located on the network. And the obvious next step should be protecting it.
How sensitive data in any organization can be protected?
- The first step is to identify which data is more sensitive in an organization's network.
- The second step is to create a backup and recovery strategy with every backup schedule.
- The last step is to establish a plan on how to recover the backup data.
Most organizations always have a backup plan in place and it is scheduled periodically. But they sometimes fail to have a plan for recovery side. The IT security management team at Proinf has the perfect plan to back up the company's data and also recover when needed, as backups are only reliable and easy when they can be recovered.
Any backup should be stored off-site in multiple locations for more security in case of a physical security breach or a natural disaster like fire, flood, etc., IT Security through backup and recovery is a basic security enhancement that every security provider performs.
Automation & Innovation
Automation in cyber security is now very much advanced and it benefits many organizations. The benefits are not just limited to the response plans but also to creating new security standards by learning from past incidents. It helps in analyzing the security landscape to understand the organization's vulnerabilities. Automation reduces human errors which can be an entry point for intrusions and breaches. Focusing on automating human-driven and repeatable processes increases productive problem-solving and fosters innovation from a cyber-security point of view. Cybersecurity initiatives are the next step in automated cybersecurity solutions.
Proinf understands and implements the next generation's ideas into its security measures. Automating the analysis, response protocols, and threat remediation replicate the expertise and reasoning of cyber experts which ensures an overall degree of greater protection and compliance.
Benefits of Automation in Cyber Security:
1. Reduced response time for any attack or intrusion
Automation significantly decreases the response time. It cuts down the time allocated for decision-making as the responses are already programmed. The saved time can be utilized for improving other security landscapes like training.
2. Reduced Human Error
Automation eliminates human errors. We can learn from the past, that human errors are attributed to many cyber incidents. Mistakes and bad judgment don't happen in automation. Cyber security is getting more advanced and some organizations benefit from automation which gave way to innovation.
3. Response Plan
Automation will ensure that the response plan is always updated and can be deployed immediately during the event of any untimed incident. In this scenario, automation can be a simple script that performs certain actions or some complex tools to run an entire response plan.
Importance of information security in an organization
We have listed a few reasons why IT security is important for an organization:
- To prove to its customers that the organization's network is stable and the customer information is safeguarded.
- Companies like Insurance providers and eCommerce need to know how their assets (transactions, credit card information, user data) are secured.
- Business operations run smoothly if the companies have consistent security practices and IT maintenance procedures.